Structure:
 The bones are classified into two divisions:
The bones are classified into two divisions:
- Axial Skeleton {This includes the skull, vertebral column (spine), and the rib cage.}
- Appendicular Skeleton {bone of upper limbs, lower limbs, and the girdles
The 5 major shapes of bones:
- Structure
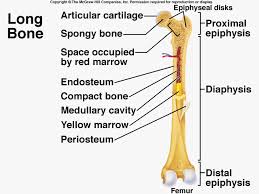
- shaft with two ends
- bone collar surrounding a hollow medullary cavity (area in the middle that holds the yellow bone marrow: fat)
- Diaphysis
- forms the long axis of the bone
- thick collar of compact bone that surrounds the medullary cavity.
- Epiphysis
- has spongy bone on the inside
- outside is covered by compact bone
- proximal is for the end closer to the center of the body
- distal is for the end that is farther away from the center of the body.
- end is covered with thin layer of articular cartilage.
- This cartilage cushions the end during the joint movement & absorbs stress.
- made of hyaline cartilage.
- Epiphyseal Line
- it is a remnant (leftover) of the epiphyseal plate (a disc of hyaline cartilage that grows during childhood to lengthen the bone).
- Periosteum
- glistening membrane that covers the entire external surface.
- Outer Layer- made of dense connective tissue (connective layer)
- Inner Layer- osteogenic (bone creating) layer and consists of osteoblasts (bone-forming cells) and osteoclasts (bone-destroying cells)
- has many nerve fibers and blood vessels which enter via a nutrient foramen.
- Secured to the underlying bone by Sharpy's Fibers ( collagen fibers that extend from the fibrous layer to the bone matrix)
- Periosteum provides anchoring points for tendons and ligaments, at these points the Sharpy's fibers are very dense.
- Endosteum
- internal surface of the bone lined with connective tissue membrane
- covers trabeculae of spongy bone in marrow cavities and lines canals that pass through compact bones.
- Osteoblast and osteoclasts are both located here.
- Ex. (femur, tibia, & phalanges)
- somewhat cube shaped
- Ex. (carpals & tarsals)
- thin, flattened
- Ex. (ribs, skull)
- have complicated shapes
- "odd men out"
- Ex. (vertebrae)
- special type of short bone in the tendon
- vary in size and number in different people
- Some of these change the direction of a pull of a tendon (something connecting a muscle to a bone)
- The function of others is not know
- Ex. (patella)
Compact Bone and Spongy Bone:
 Compact Bone-
Compact Bone-
- This external layer of the bone is very thick and looks smooth.
Spongy Bone
- This part of the bone contains many holes and contains small flat pieces called trabeculae.
- These spaces within the between the trabeculae are filled with marrow (both red and yellow) in living bones.
Function:
There are 5 major functions of bones and these include:
- Support the body and cradle the organs
- Protect vital organs
- Allow movement
- Store Minerals (we like us some calcium and phosphate!)
- Hematopoiesis (it is the formation of red blood cells)
 The bones are classified into two divisions:
The bones are classified into two divisions: Compact Bone-
Compact Bone-
No comments:
Post a Comment